clinical test for testicular torsion|testicular torsion signs on examination : inc A negative Prehn's sign, or exacerbation of pain upon elevation of the testicle, is one of the clinical features of testicular torsion. This occurs when the testicle rotates and compresses the spermatic cord (i.e., bundle of fibers . web7 de mar. de 2022 · Garena. Garena https://ff-advance.ff.garena.com/. Faça login utilizando o mesmo método do Free Fire — Foto: Reprodução/Igor Dantas. Preencha as .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB21 de fev. de 2024 · Como Fazer o Depósito na GGbet via PIX? Sem dúvida nenhuma, depositar no Pix é a forma mais prática e rápida de ter seu dinheiro disponível em conta. Além disso, é totalmente gratuito para .
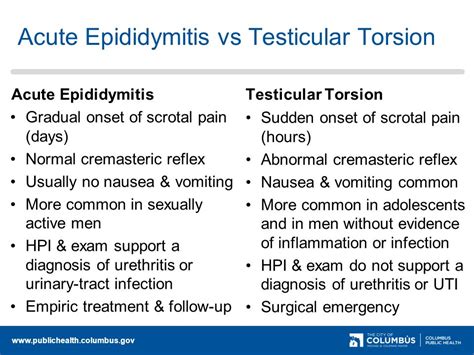
Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a.Individual clinical findings that best predict testicular torsion include nausea and . A negative Prehn's sign, or exacerbation of pain upon elevation of the testicle, is one of the clinical features of testicular torsion. This occurs when the testicle rotates and compresses the spermatic cord (i.e., bundle of fibers .
Individual clinical findings that best predict testicular torsion include nausea and vomiting, past trauma, a tender testicle, an abnormal testicular lie (i.e., elevated or transverse),. Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischemia, . Typical clinical findings on testicular examination may include: Inflammatory signs of one testis: swollen, tender and erythematous scrotal skin Lie of the testis might be horizontal (in a ‘bell-clapper’ position) and high .What tests will be done to diagnose testicular torsion? Your healthcare provider may order a scrotal ultrasound to determine if blood is flowing within your testicular tissues. A scrotal .
Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal . laboratory test results Hard mass within testicle Systemic symptoms (if .
testicular torsion vs epididymitis signs
A diagnosis of testicular torsion should be suspected in any person presenting with acute scrotal pain and/or swelling, . Assess the need to test for a UTI with a urine dipstick test and mid-stream urine . Clinical features; Testicular cancer: Usually unilateral testis enlargement, or change in shape or texture (often painless, may be dull .If a person has sudden-onset scrotal pain and testicular torsion is suspected clinically, arrange emergency hospital admission to urology or paediatric surgery, depending on clinical judgement.; If a person has no current scrotal swelling or pain, but has a history of previous episodes of severe, self-limiting scrotal pain or swelling, arrange a urology referral, the urgency depending . Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischemia, and/or necrosis of testicular tissue. Laher A, Ragavan S, Mehta P, et al. Testicular torsion in the emergency room: A review of detection and management strategies.Testicular torsion causes your testicle to twist and cuts off its blood supply. It causes severe pain and requires emergency care. . What tests will be done to diagnose testicular torsion? Your healthcare provider may order a scrotal ultrasound to determine if blood is flowing within your testicular tissues. A scrotal ultrasound is a quick .
A comparison of clinical outcomes of acute testicular torsion between prepubertal and postpubertal males. J Pediatr Urol. 2019 Dec. 15 (6):610-616. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. Alzahrani MA, Alasmari MM, Altokhais MI, Alkeraithe FW, Alghamdi TA, Aldaham AS, et al. Is There a Relationship Between Waking Up from Sleep and the Onset of Testicular Torsion?.
testicular torsion survival rate
Testicular torsion occurs when a testis torts on the spermatic cord resulting in the cutting off of blood supply. . Differentiation between testicular torsion and epididymo-orchitis is a clinical challenge, since scrotal pain, swelling, and redness or tenderness are clinical symptoms common to these two entities. On this page: Laboratory tests are unlikely to be of consequence, as no single test has high sensitivity or specificity in diagnosing testicular torsion. However, when there is a strong suspicion of an alternative diagnosis, laboratory tests may be of some use. . scoring system was developed for the purpose of determining the risk of testicular torsion on .
Each year, testicular torsion affects one in 4,000 males younger than 25 years. Early diagnosis and definitive management are the keys to avoid testicular loss. All prepubertal and young adult .
The diagnosis is mostly clinical, based on the presentation of the signs and symptoms of testicular torsion. . Additional diagnostic methods include urine tests to exclude infection, scrotal ultrasound (color Doppler) showing absent or decreased blood flow to the affected testicle, or even surgery to explore the area and confirm the diagnosis .Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord (from which the testicle is suspended) twists, cutting off the blood supply to the testicle. [3] The most common symptom in children is sudden, severe testicular pain. [1] The testicle may be higher than usual in the scrotum and vomiting may occur. [1] [2] In newborns, pain is often absent and instead the scrotum may become .
American Urological Association Curriculum on Acute Scrotum: This case-study offering from the association's medical school curriculum covers the differential diagnosis of acute scrotum with a concentration on 6 conditions: epididymitis, hernia, scrotal trauma, testicular torsion, testicular tumor, and torsion of testicular appendices. Pediatric testicular torsion: demographics of national orchiopexy versus orchiectomy rates. J Urol. 2011 Jun. 185 (6 Suppl):2459-63. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. Goetz J, Roewe R, Doolittle J, Roth E, Groth T, Mesrobian HG, et al. A comparison of clinical outcomes of acute testicular torsion between prepubertal and postpubertal males. Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, typically presenting with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. . scintigraphy using Technicium 99 pertechnate injected intravenously on an emergency basis is a valid and reliable test to diagnose testicular torsion whenever clinical and sonological findings are inconclusive [3,4].
custom how to use a grain moisture meter
Clinical Practice Guidelines. Toggle section navigation. . Testicular torsion is an emergency. It requires immediate referral to a surgeon . Blood tests, ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound are not useful in the acute setting; Once testicular torsion and irreducible hernia have been confidently excluded, ultrasound may be considered if the . Testicular torsion is a urological emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischaemia, and/or necrosis of testicular tissue. Laher A, Ragavan S, Mehta P, et al. Testicular torsion in the emergency room: A review of detection and management strategies.
Torsion of the testis is a surgical emergency. Although it occurs in all age groups, torsion is most common in adolescents. The typical presentation is with a tender, swollen scrotum and lower abdominal pain; symptoms are however variable and often much less marked in young children and neonates. How common is testicular torsion? Testicular torsion occurs in teenage boys aged 13-18 years. This is found to happen in around 1 in 4,000 young men. Newborn babies and younger children sometimes develop this problem. It is uncommon over the age of 25 but does occur sometimes in older adults and can occur at any age.Clinical Features. History: Abrupt onset testicular pain associated with nausea or vomiting; May have previous similar intermittent, self-resolving episodes; . ↑ Barbosa, JA, et al. Development of initial validation of a scoring system to diagnose testicular torsion in children. The Journal of Urology. 2013; 189:1853-8.
1. Introduction. Acute scrotum or testicular pain is one of the most important problems in the emergency department (ED). Acute scrotum is defined as a sudden onset scrotum pain with or without edema and tenderness, which is a true surgical emergency due to the possibility of testicular torsion (1, 2).There are a wide range of differential diagnoses for .American Urological Association Curriculum on Acute Scrotum: This case-study offering from the association's medical school curriculum covers the differential diagnosis of acute scrotum with a concentration on 6 conditions: epididymitis, hernia, scrotal trauma, testicular torsion, testicular tumor, and torsion of testicular appendices. Purpose: Analyze the clinical manifestations, laboratory tests, and imaging data of testicular torsion to provide clinical insights for timely and accurate diagnosis and treatment of testicular torsion. Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on the clinical data of 67 The cremasteric reflex has been reported to be absent in 100% of cases of testicular torsion, making it a potentially useful sign in this diagnosis. However, a significant number of case reports and small case series exist, demonstrating that the test is not 100% specific, and the reflex can be present in cases of testicular torsion.
custom how to use a lumber moisture meter
Answer: Testicular torsion 1-15. Epidemiology. Bimodal incidence: 1 st year of life and teenage years (12-18 years) 1,2; Rare case reports of men age > 40 years with cases of testicular torsion 1,2; 50% of patients with testicular torsion have a previous episode of torsion that spontaneously resolved 3; Testicular pain accounts for 1% of ED visits annually 1 .Failure to promptly reduce torsion may result in infertility from ischemic loss of germ cells or the generation of anti-sperm antibodies.1 Although most common in neonates and pre-pubertal males, torsion may occur at any age with nearly 40% outside typical demographics.2 In the United States, testicular torsion occurs 5.9 times per 100,000 . Introduction. Testicular torsion is commonly encountered in pediatric scrotal emergencies and occur at various age groups. The etiology is not fully elucidated, often attributed to anomalies in the anatomical structure of the testis or spermatic cord, or excessive mobility of the testis leading to torsion (1, 2).Its clinical manifestations are diverse, with common typical .Scrotal and testicular masses can be broadly categorized into painful conditions, which include testicular torsion, torsion of the testicular appendage, and epididymitis, and painless conditions .

testicular torsion signs on examination
Endereço Av. Deputado Benedito Matarazzo, 9403 Jardim O.
clinical test for testicular torsion|testicular torsion signs on examination